Electricity can be used as a transportation fuel to power plug-in battery electric vehicles. Using electricity from the grid to run vehicles costs less and reduces petroleum consumption and associated tailpipe emissions compared to conventional fuel. Electricity for vehicle battery charging can come from the existing power grid or from distributed renewable sources such as solar or wind energy.
Electric Vehicles
There are three types of electric vehicles on the market: Plug-in Electric Vehicles (PEVs or EVs), Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs), and Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs).
Plug-in Electric Vehicles (EVs) are all-electric, battery-powered vehicles, commonly known as EVs. PEVs run on a battery that is charged by plugging the vehicle into charging equipment. This type of electric vehicle cannot run on any form of fuel other than electricity. EVs always operate in all-electric mode and have typical driving ranges of 150 to 300 miles.
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) are powered by both conventional fuel as well as electricity stored in a battery. PHEVs can operate in all-electric (or charge-depleting) mode for between 20 and 40 miles. After the battery is depleted, PHEVs will operate solely on conventional fuel.
Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) cannot be plugged in and are powered by an internal combustion engine that runs on conventional fuel. HEVs differ from conventional vehicles by storing energy in a battery through regenerative braking, whereby kinetic energy is captured though the wheels as the car slows down. The energy stored in the battery from regenerative braking assists the engine in HEVs, providing increased fuel economy compared to conventional vehicles.
EV Charging
Oklahoma has an extensive electric vehicle charging network. The farthest distance between fast chargers along major Oklahoma highways and interstates is only 70 miles. Check out chargers along your everyday routes using the Station Locator below.
How Does Charging Work?
Instead of making a trip to a gas station, EV drivers charge wherever they already are.
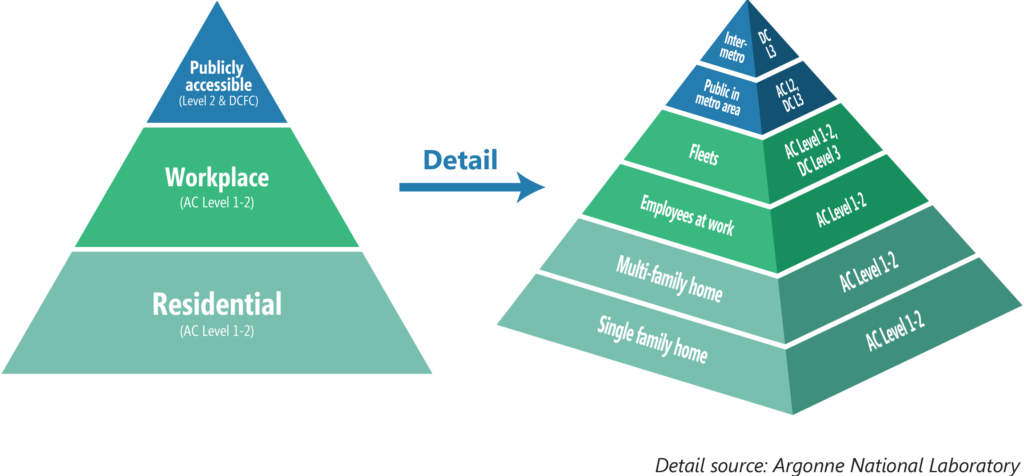
At-Home Charging: Most plug-in electric vehicle owners do the majority of their charging at home using a common three-prong household outlet. 80-90% if charging happens at home!
Workplace Charging: Employers can help increase the convenience and affordability of driving electric for their employees, attract and retain a cutting-edge workforce, and demonstrate leadership in adopting advanced technologies by providing workplace charging.
Public Charging: EV owners rely on public DC fast charging along highway routes when taking longer distance trips.
Level 1 Charging (AC L1)
2 to 5 miles of range per
1 hour of charging
Provided by a common three-prong, 120V household outlet
Level 2 Charging (AC L2)
10 to 20 miles of range per 1 hour of charging
Provided by 240V outlets (dryer outlet) and dedicated Level 2 charging stations
Most common charging level for daily driving, ideal for single family homes, multifamily buildings, and workplaces
DC Fast Charging (DCFC/L3)
60 to 80 miles of range per
20 minutes of charging
High-power dedicated stations usually located along heavy traffic corridors
Used primarily on long-distance trips
Explore EV Charging Stations in the Tulsa Area
The U.S. Department of Energy provides a Station Locator tool on the Alternative Fuels Data Center (AFDC). This tool is maintained by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory using information collected by Clean Cities and Communities coalitions across the country.
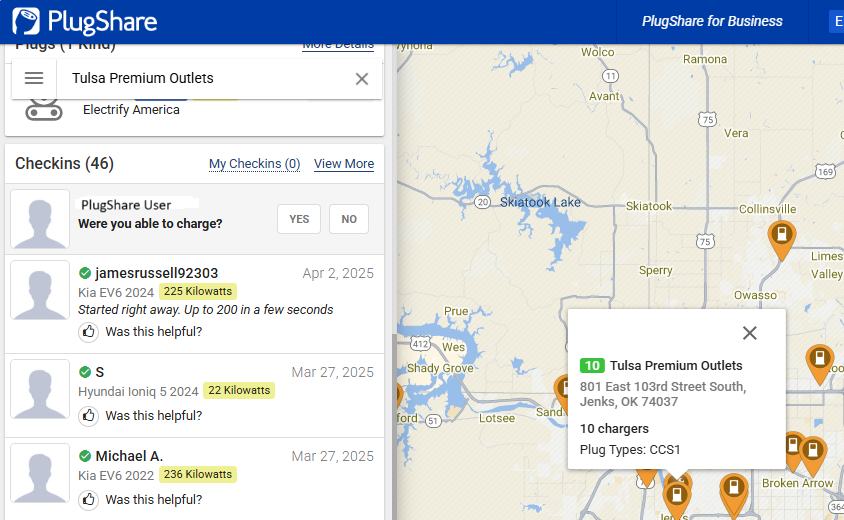
PlugShare is a popular tool for finding EV charging stations, available on desktop or through the PlugShare app. PlugShare provides an array of filter options that allow users to sort stations by power delivery, ratings, amenities, and more.
PlugShare allows users to leave reviews (called “checkins”) and ratings for stations they’ve visited.
By checking recent reviews and ratings ahead of time, EV drivers can avoid stopping at stations with issues.
A Better Routeplanner (ABRP) can help EV drivers optimize their trips and avoid range anxiety. Available via desktop or mobile app, ABRP takes into consideration your vehicle model, starting state of charge, and the exact route you’ll be taking to identify the best stops to charge and calculate a close estimate of the battery level you’ll be left with at the end of your trip.
EV Registration in Oklahoma
Total Statewide EV Registrations (2023) = 22,800
Oklahoma Light-Duty EV & PHEV Registration Counts by Year
For historical data, visit the AFDC.
Oklahoma’s EV Economy
- Founded in 2015 and headquartered in Tulsa, Oklahoma, Francis Energy has rapidly grown to become the fourth largest privately held charging network in the country.
- Spiers New Technologies, acquired by Cox Automotive in 2021, is an industry leading full-service provider of remanufacturing, refurbishment, repair, reuse, and recycling for advanced battery packs used in hybrid and electric vehicles with core operations in Oklahoma City.
- IC Bus (Navistar) is the nation’s largest manufacturer of school buses and builds their CE Series electric bus models in Tulsa.